RADIANT CATALYTIC IONIZATION
Combining the power of the sun with geometry from the hives of bees, Radiant Catalytic Ionization (RCI) is a potent method to help purify the air. When the device is turned on, a UV lamp inside the device turns on. It emits UV radiation, which hits a honeycomb matrix within the device. This honeycomb structure, copied from one of Nature’s incredible creations built by bees, is very strong/robust and increases the surface area which comes into contact with the UV radiation.
This structure is coated with titanium dioxide (TiO₂) and helps to increase the speed of the chemical processes. Inside this honeycomb matrix, processes which create superoxide and hydroxide ions are started. When the UV radiation hits this honeycomb matrix, photocatalysis takes place. “Photo” refers to light, and a “catalyst” is something that speeds up a chemical process. So the light speeds up the processes taking place.
The ions that are created in this way eliminate the pollutants which are close to the honeycomb matrix, and when they exit the device they still act outside as “purifying plasma.” This means that even when they exit the device, they continue to destroy microorganisms, oxidize gaseous organic compounds and remove unwanted smells inside rooms.
HOW DOES RCI WORK?
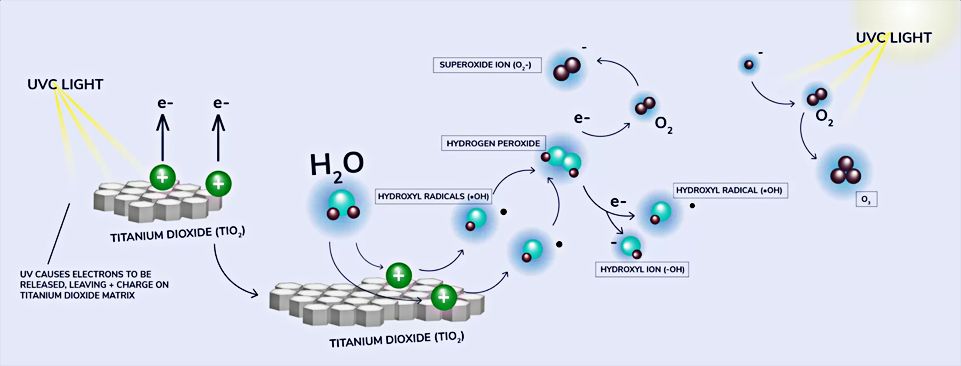
- A honeycomb shaped matrix coated with titanium dioxide (TiO₂) inside the device allows maximum surface area for UV light exposure
- UVC light from a UV lamp shines on this matrix at the right wavelength to release electrons from the TiO₂, leaving a positive charge on the matrix (hydrophilic - attracting water)
- Reactions occur to generate the following reactive oxygen species (ROS):
- Hydroxyl Radicals (·OH): Formed by electron being taken from water by + charge on the TiO₂ matrix
- Superoxide Ion (O₂-): Formed by a released electron reacting with O₂
- Hydrogen Peroxide (H₂O₂): Formed by two hydroxyl radicals combining.
- O₃: Formed by the UV light splitting O₂. Resulting O- joins another O₂ to form O₃
HYDROXYL RADICAL
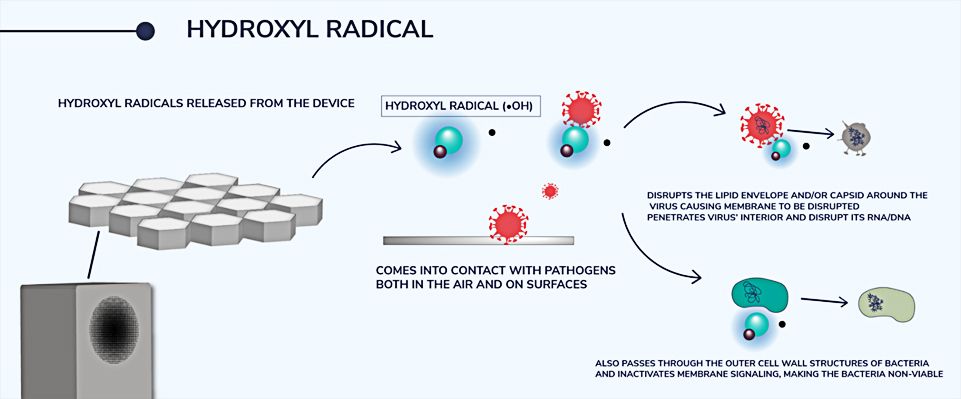
- Hydroxyl radicals released from the device
- Comes into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces
- Disrupts the lipid envelope and/or capsid around the virus causing membrane to be disrupted
- Penetrates virus’ interior and disrupt its RNA/DNA
- Also passes through the outer cell wall structures of bacteria and inactivates membrane signaling, making the bacteria non-viable.
SUPEROXIDE
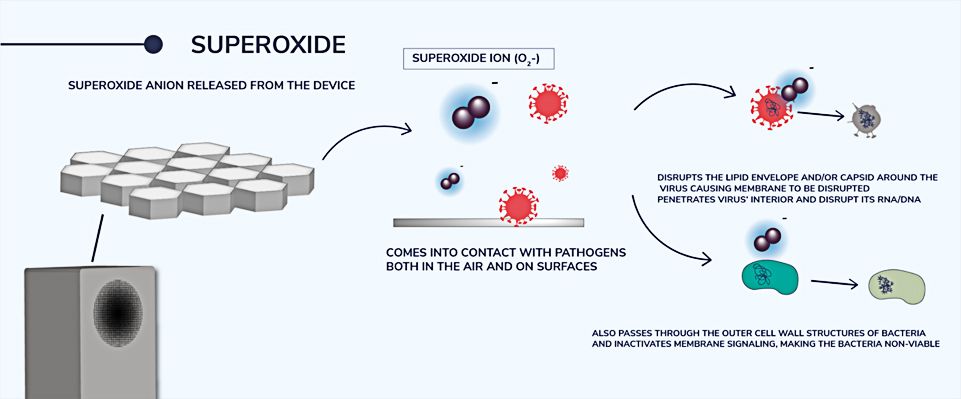
- SuperOxide anion released from the device
- Comes into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces
- Disrupts the lipid envelope and/or capsid around the virus causing membrane to be disrupted
- Penetrates virus’ interior and disrupt its RNA/DNA
- Also passes through the outer cell wall structures of bacteria and inactivate membrane signaling, making the bacteria non-viable.
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
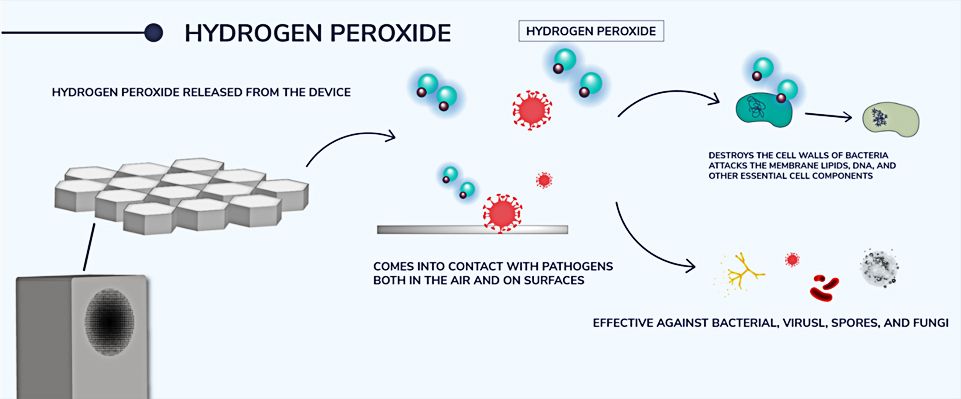
- Hydrogen peroxide released from the device
- Comes into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces
- Destroys the cell walls of bacteria Attacks the membrane lipids, DNA, and other essential cell components
- Effective against bacterial, viruses, spores, and fungi
TRIOXYGEN
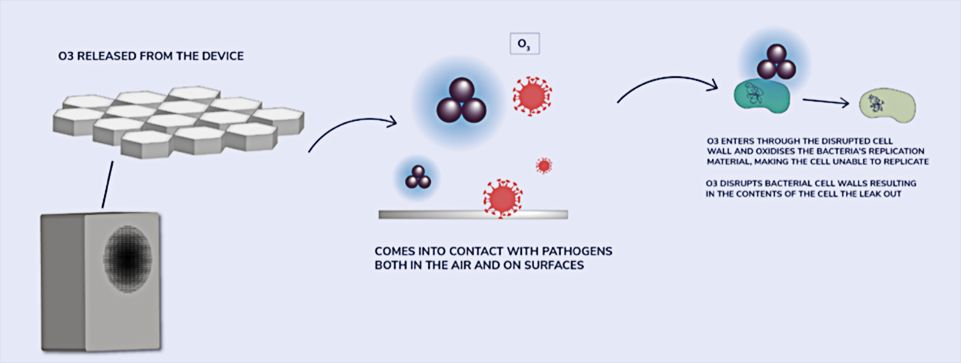
- O₃ released from the device
- Comes into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces
- O₃ enters through the disrupted cell wall and oxidises the bacteria’s replication material, making the cell unable to replicate
- O₃ disrupts bacterial cell walls resulting in the contents of the cell the leak out

