Blog
How to Prepare Your Home for Poor Air Quality Days
Learn how to protect your home from poor air quality with EcoQuest’s Fresh Air Black, OzoneWater by LT&B, and Robotic...
Details
Wearable Air Purifiers: A New Trend for U.S. Commuters and Outdoor Workers
Discover the rise of wearable air purifiers in the U.S., perfect for commuters and outdoor workers.
Details
Air Purifiers with Humidification and Ionization: Benefit or Risk?
Discover the pros and cons of air purifiers with humidifiers and ionizers. Is it a healthy choice or a hidden risk? We...
Details
What Is Pet Dander and How to Remove It from Your Home
Learn what pet dander is, how it affects your health, and how EcoQuest air purifiers eliminate it
Details
How to Protect Your Home from Wildfire Smoke with Air Purifiers
Learn how to protect your home from wildfire smoke with air purifiers. Discover EcoQuest’s HEPA and activated carbon...
Details
The Impact of Air Quality on Sleep: Can Air Purifiers Help You Rest Better?
Discover how poor air quality impacts your sleep and how air purifiers can help improve rest by removing allergens,...
Details
How Indoor Plants and Air Purifiers Work Together to Improve Air Quality
When it comes to improving indoor air quality, both air purifiers and houseplants are popular solutions. But did you...
Details
Comparing Air Purification Technologies: HEPA, Activated Carbon, and UV-C Light
With so many air purification technologies available, choosing the right one for your needs can feel overwhelming. HEPA...
Details
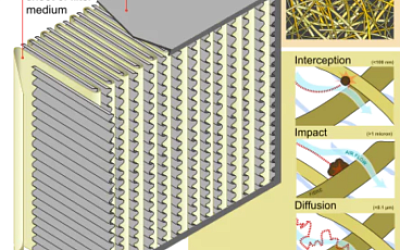
The Science Behind HEPA Filters: How They Trap Allergens and Pollutants
When it comes to maintaining clean indoor air, HEPA filters are among the most trusted technologies available. But how...
Details
Ionic Air Purifiers and Ozone: What You Need to Know
Learn the differences between ionic air purifiers and ozone generators. Discover how EcoQuest’s ozone technology...
Details
How to Relieve a Stuffy Nose at Night for Better Sleep
Struggling with a stuffy nose at night? Learn how EcoQuest’s air purifiers reduce allergens and improve air quality for...
Details
11 Ways to Stay Healthy During Flu Season
Discover 11 effective ways to stay healthy during flu season. Learn how EcoQuest’s air purifiers can reduce airborne...
Details
How to Remove Smelly Dog Odors: A Complete Guide for Pet Owners
Tired of dog odors in your home? Learn how EcoQuest’s air purifiers with ozone technology eliminate pet smells and...
Details
Why Hotels Need Air Purifiers: Creating a Cleaner, Healthier Guest Experience
Learn how air purifiers can elevate the guest experience in hotels. Discover EcoQuest’s solutions for eliminating...
Details



.jpg)